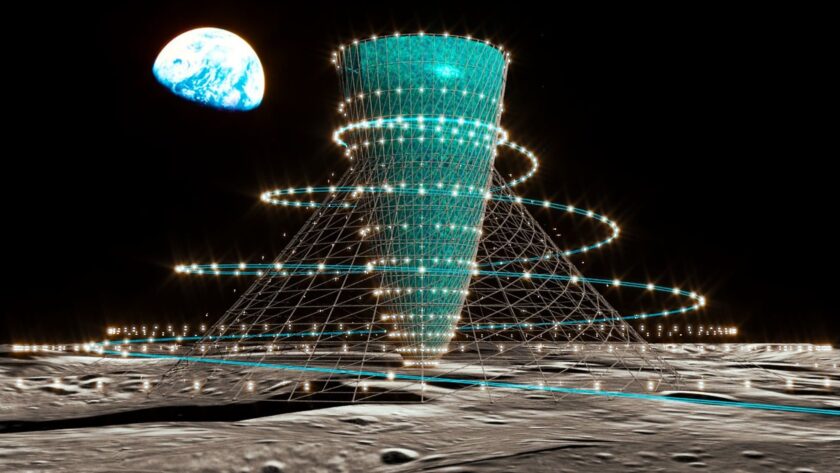
There is no shortage of research that explores the effects of life in gravity that is lower than the earth, with one of the main concerns is reducing bone mass, but the problem reaches a completely new level in terms of supporting several generations born and raised in such conditions. This concern presents a strange dilemma for scientists who imagine the future where people live on the moon or mars – the future in which humanity needs to overcome the gravitational situation, of course. In an effort to solve this critical problem, the Japanese team of scientists have proposed to build a cone and livable structure in a rotating month to produce gravitational forces with the same magnitude as the earth’s natural gravitational pull.
Experts from Kyoto University, in collaboration with people at Kajima Construction Co. Ltd., provides a virtual presentation that detailed the structure called Lunar Glass. This concept is basically a reverse cone that rotates to make the centrifugal pull mimic the effects of the actual gravity of the earth. The height of about 1,300 feet and with 328 feet fingers, the researchers hope to build a simplified prototype version of 2050, according to Asahi Shimbun. Regarding the final version that can support several generations, it takes about a full century to be built. In addition to the moon, the team also talked about the gravitational residence made by parallel for humans on Mars, precisely called Mars Glass.
Futuristic end to end solution
.
Called the first idea of its type, the team did not stop just building bases on the Moon and Mars. Interestingly, the concept of Lunar and Mars Glass is just one part of a larger project; Centerpiece is a transportation system between the earth and its purpose that will maintain the gravity of the earth when transporting passengers.
Nicknamed the Space Space Trek System, basically this is an interplanet transportation system such as trains that will support business and tourism activities. In an era where billionaires have spent hundreds of millions for space joyrides, tourism activities on space trains that like gravity to the moon or not sound too far. The track station on Earth is dubbed Terra Station, while the Space Express train engaged in the standard measuring route will have six coaches.
Leading cars and trailing cars will have a rocket booster tied to them. Hexagonal passenger capsules and will come in two sizes with fingers each of them around 50 and 100 feet. The capsule will move next to the central radial axis to produce the same gravitational pull as the planet Earth. However, Lunar Glass is not the first project of its type. In 1975, Stanford University experts presented a concept called Stanford Torus in Nasa Summer Study; It is imagined as a donut -shaped ring that is slightly more than one mile with a diameter and should accommodate anywhere between 10,000 to 140,000 residents.